

Abstract: In this work, we upgrade FireRedTTS to a new version, FireRedTTS-1S, a high-quality streaming foundation text-to-speech system. FireRedTTS-1S achieves streaming speech generation via two steps: text-to-semantic decoding and semantic-to-acoustic decoding. In text-to-semantic decoding, a semantic-aware speech tokenizer converts the speech signal into semantic tokens, which can be synthesized from the text via a language model in an auto-regressive manner. Meanwhile, the semantic-to-acoustic decoding module simultaneously translates generated semantic tokens into the speech signal in a streaming way. We implement two approaches to achieve this module: 1) a chunk-wise streamable flow-matching approach, and 2) a multi-stream language model-based approach. They both present high-quality and streamable speech generation but differ in real-time factor (RTF) and latency. Specifically, flow-matching decoding can generate speech by chunks, presenting a lower RTF of 0.1 but a higher latency of 300ms. Instead, the multi-stream language model generates speech by frames in an autoregressive manner, presenting a higher RTF of 0.3 but a low latency of 150ms. In experiments on zero-shot voice cloning, the objective results validate FireRedTTS-1S as a high-quality foundation model with comparable intelligibility and speaker similarity over industrial baseline systems. Furthermore, the subjective score of FireRedTTS-1S highlights its impressive synthesis performance, achieving comparable quality to the ground-truth recordings. These results validate FireRedTTS-1S as a high-quality streaming foundation TTS system.
System Overview
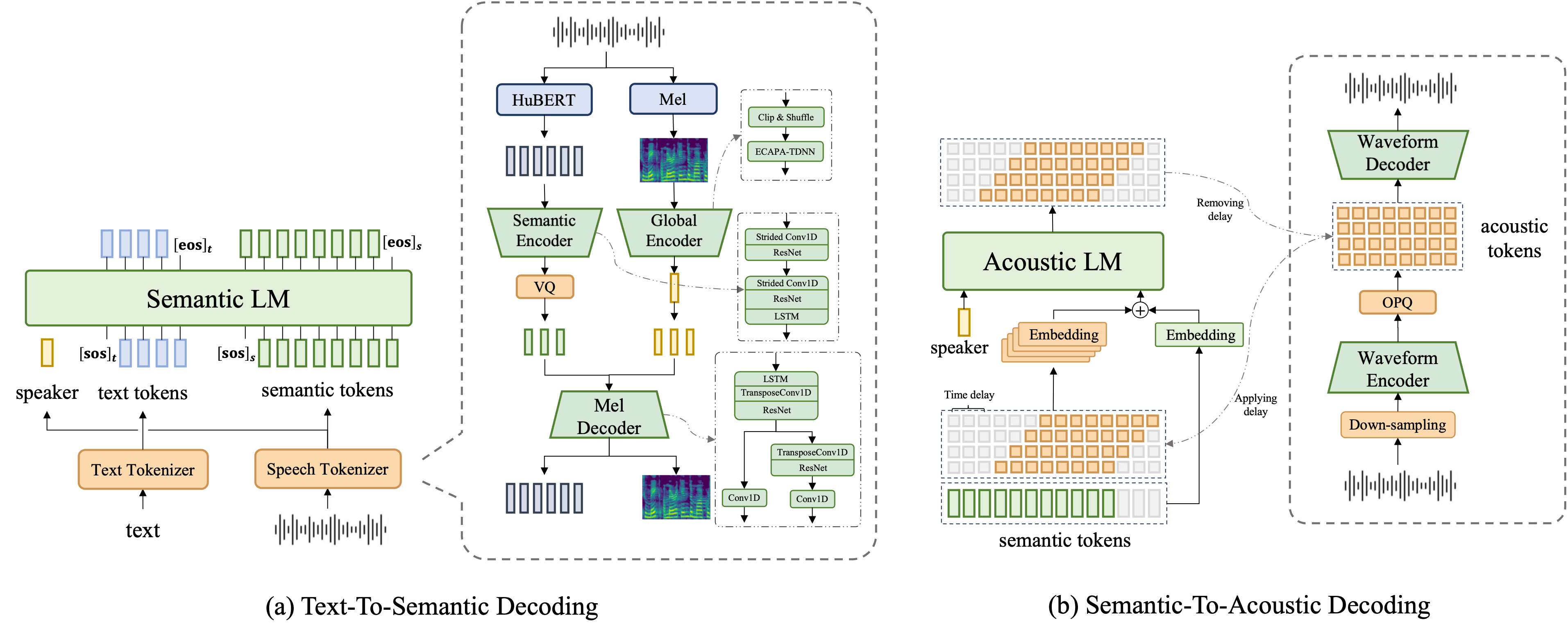
Figure 1. An overview of the FireRedTTS-1S: In text-to-semantic decoding, a speech tokenizer is trained to extract semantic tokens and speaker embedding from the speech audio, and a semantic language model generates semantic tokens from the input text sequence and the speaker embedding from the reference audio. In semantic-to-acoustic decoding, we implement two approaches to translate semantic tokens into the speech waveform in a streaming way. In (c), we empower the flow-matching approach with the streamable decoding capability. In (d), a multi-stream acoustic LM with a "delay pattern" is trained to map semantic tokens into the multi-stream acoustic token sequence, which is encoded from the speech signal and decoded back by the acoustic codec.
Voice Cloning
Zero-Shot In-Context Learning
| Prompt | CosyVoice 2 | FireRedTTS1 | FireRedTTS1S-LM | FireRedTTS1S-FM | Ground Truth |
|---|